Rearch Interest: Visualization">
My Test
Hi this is a quick test for my post!
Here's the Title
And here is the content.
Hi this is a quick test for my post!
And here is the content.
Title: Developing a Single Page App with Flask and Vue.js Author: Michael Herman Origin: https://testdriven.io/blog/developing-a-single-page-app-with-flask-and-vuejs/#vue-setup Note: 原作者用的是Vue2,我用的是Vue3,但是在本应用中区别不大。
本文指示了如何基于Flask+Vue.js构建一个支持基本CRUD操作 (增删查改) 的应用。 (本文只大致翻译到了打通前后端的部分。后续内容可在原博客查看。)
Flask是一个简单而强大的基于Python的微型Web框架,非常适合于构建表现层状态转移API (RESTful APIs)。 像 Sinatra (Ruby) 和 Express (Node) 一样,它非常小巧灵活,所以你可以从小开始按照需求逐步构建一个复杂的应用。
Vue是一个开源的JavaScript框架,用于构建用户界面。 它采用了React和Angular的一些长处。也就是说,与React和Angular相比,它更加平易近人,所以初学者可以快速上手。 它也同样强大,所以它提供了你创建现代前端应用程序所需的所有功能。
首先准备好项目根目录 flask-vue-crud。
1 | $ mkdir flask-vue-crud |
在文件夹 flask-vue-crud 中,创建一个新的目录
server。 然后,我们在 server
目录下创建并激活虚拟环境。
1 | $ python -m venv env |
安装Flask和Flask-CORS扩展。
1 | (env)$ pip install Flask==1.1.2 Flask-Cors==3.0.10 |
在 server 目录下创建 app.py。
1 | from flask import Flask, jsonify |
为什么需要安装 Flask-CORS ?
- 为了进行跨源请求 (cross-origin requests)——例如,来自不同协议、IP地址、域名或端口的请求——因此需要启用跨源资源共享(CORS, Cross Origin Resource Sharing)。Flask-CORS为我们处理这个问题。
- 值得注意的是,上述设置允许所有路由的跨源请求,来自任何域、协议或端口。在生产环境中,你应该只允许来自前端应用程序所在域的跨源请求。——Flask-CORS文档
接下来,我们运行 app.py:
1 | (env)$ python app.py |
然后我们可以在浏览器的 http://localhost:5000/ping 看到测试的结果。页面上应该出现:
1 | "pong!" |
于是我们就可以在命令行用 Ctrl+C 杀死服务器,并回到项目的根目录
flask-vue-crud, 准备Vue的设置。
Note: 作者采用的是Vue2,这里使用的是Vue3.
我们将采用 Vue CLI来生成一个定制的项目模板。 全局安装。
1 | $ npm install -g @vue/cli@4.5.11 |
然后,在项目根目录flask-vue-crud
下,运行下列命令初始化一个名为 client 的 Vue 项目。
1 | $ vue create client |
需要手动选择一些选项。
1 | Vue CLI v4.5.11 |
选择 Manually select features.
接下来,选择Choose Vue version, Babel,
Router, 和 Linter / Formatter。
1 | Vue CLI v4.5.11 |
1 | Vue CLI v4.5.11 |
这样项目就构建完成了。
所生成的项目可能包含很多内容,但我们只会处理
src 目录下的内容和
public目录下的index.html。
文件index.html 将会是 Vue 应用的起点。
其中,有一个id="app"的div元素。
这是一个占位符,Vue会将所生成的HTML和CSS附在上面,以产生UI。
接下来,我们来看看 src目录下的构造。
1 | client/src |
我们来看看 component目录下的HelloWorld.vue
文件。 这是一个单文件组件 (Single File component), 分为 3 个部分:
让我们来启动开发服务器。
1 | $ cd client |
在浏览器中打开 http://localhost:8080 。你应该看到如下的页面。

为了让事情简单一点,我们移除文件夹 client/src/views。
然后,在
client/src/components目录下添加一个叫Ping.vue的组件。
1 | <template> |
然后,更新
client/src/router/index.js以将/ping映射到刚刚创建的Ping组件。
1 | import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router'; |
最后,在 client/src/App.vue
中,移除navigation和样式表。
1 | <template> |
此时,你应该在http://localhost:8080/ping的页面上看见Hello!。
Error: Expected linebreaks to be 'LF' but found 'CRLF' linebreak-style Solution: 将所有
.eslintrc的'linebreak-style'改成'linebreak-style': ['error', 'windows']。
为了连接前端的Vue应用和后端的Flask应用,我们可以使用 axios 库来发送 AJAX 请求。 首先,我们安装它。
1 | $ npm install axios@0.21.1 --save |
然后,我们更新组件 Ping.vue 中的 script
部分。
1 | <script> |
在命令行中启动Flask侧的应用。你应该可以在页面上看到pong!.
基本的做法是,当后端返回一个response时,我们将msg设置为response对象的data值。
接下来,我们将Boostrap配置到我们的应用上。这是一个流行的CSS框架。
安装
(忽视关于jquery和popper.js的警告。不要把它们添加到你的项目里):
1 | $ npm install bootstrap@4.6.0 --save |
将Boostrap样式表添加到client/src/main.js。
1 | import { createApp } from 'vue'; |
在client/src/App.vue的样式表部分进行更新。
1 | <style> |
在组件Ping中,使用Button和Container确保Boostrap被正确地配置。
1 | <template> |
运行开发服务器后,你应该看到这样的画面:

接下来,在/components目录下新建Books.vue文件并增加一个名为Books的组件。
1 | <template> |
更新路由:
1 | import Vue from 'vue'; |
测试以下两个链接:
然后,我们在Books组件中增添一个Boostrap样式的表格。
1 | <template> |
你应该看到:

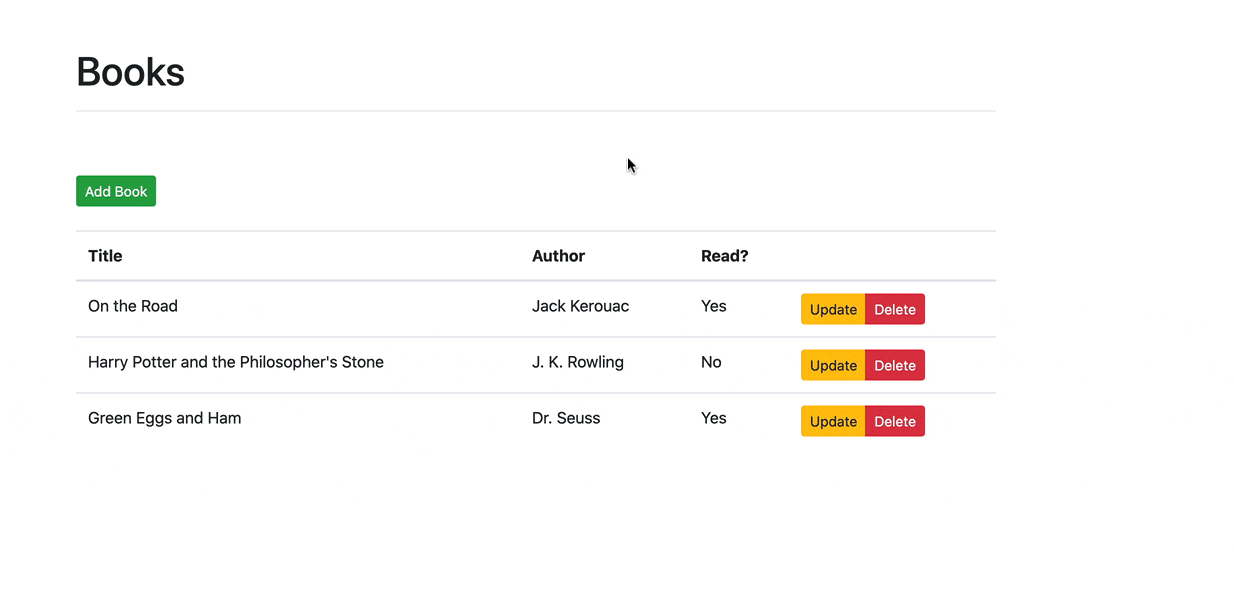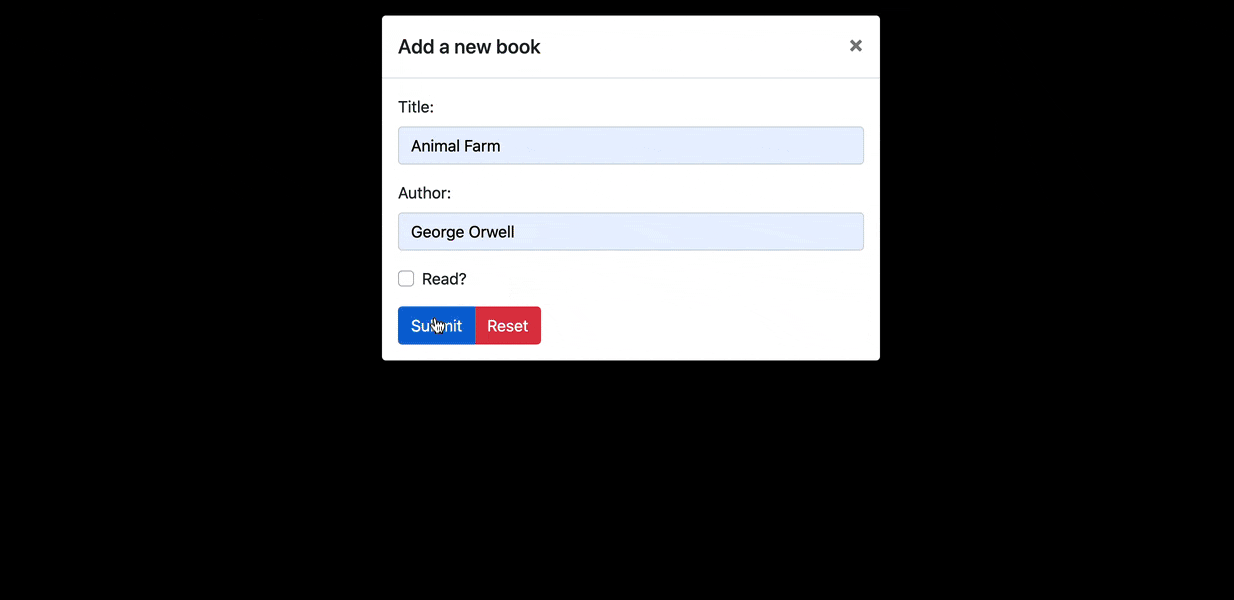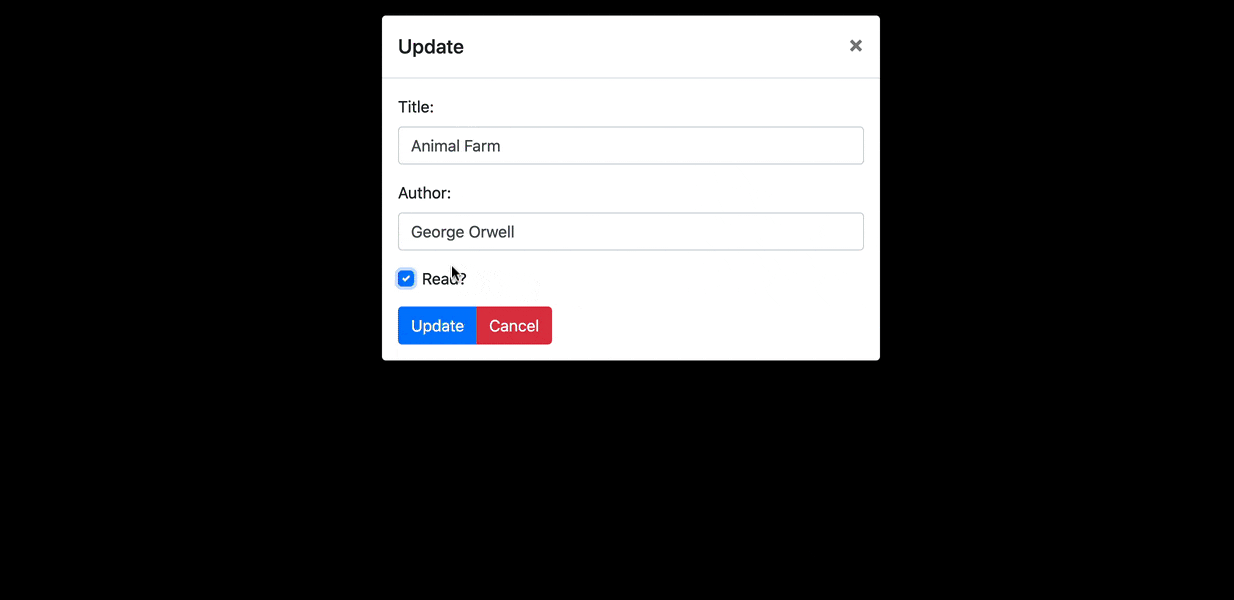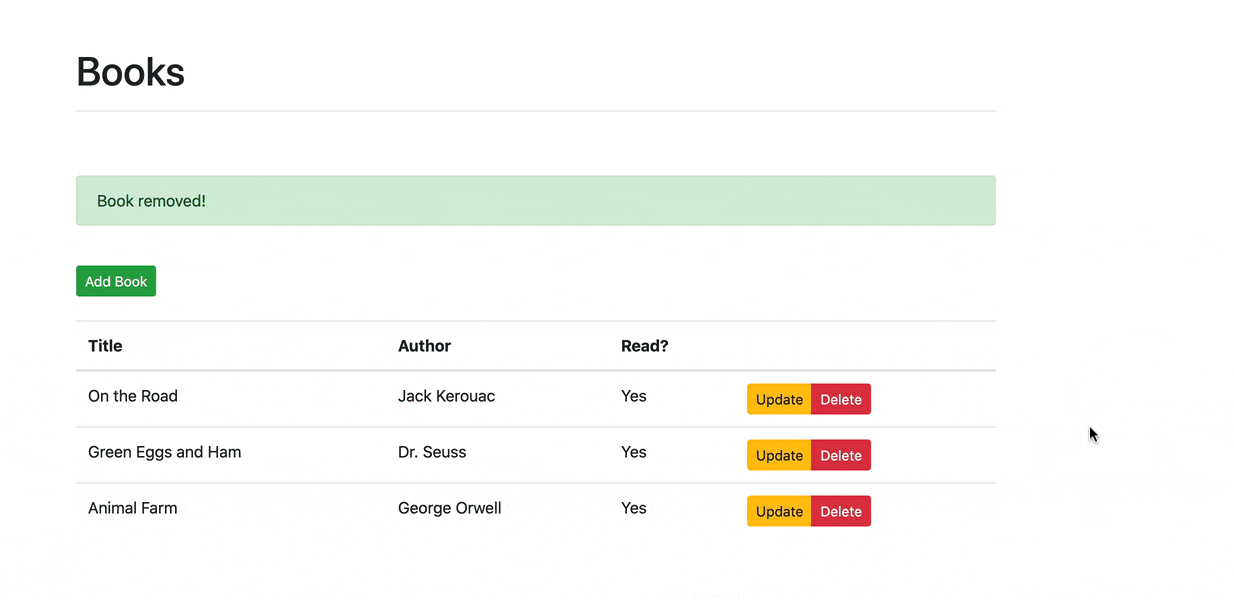
现在,我们终于可以开始实现我们的CRUD应用的功能部分了。
我们的目标是设计一个后端表现层状态转移API (RESTful APIs), 由Python和Flask驱动,用于一个单一的资源—— Books。 该API本身应遵循RESTful设计原则,使用基本的HTTP动作: GET、POST、PUT和DELETE。
我们还将用Vue建立一个前端应用程序,以使用后端API。

在 server/app.py 中 添加一个书的list。
1 | BOOKS = [ |
并且添加路由handler:
1 | @app.route('/books', methods=['GET']) |
此时,运行该Flask
app的话,你应该可以在http://localhost:5000/books看到这个list。
更新组件:
1 | <template> |
当组件初始化完毕,生命周期钩子(lifecycle hook)
created将会触发函数getBooks(),
以从我们刚刚设置的后端处获取Books。
在该模板中,我们通过v-for指令遍历 books
的list,在每次遍历中创建一个新的表行。
索引值被用来作为key。
最后,v-if被用来呈现Yes或No,表明用户是否已经阅读了这本书。

在下一节中,我们将使用一个modal来添加新书。 我们将为此添加Bootstrap Vue库,它提供了一套用基于Bootstrap的HTML和CSS进行样式定制的Vue组件。
这个库目前不支持Vue3,所以没有再搞了。
GitHub Docs当中关于这部分的翻译。
不要添加最后的README, license, 以及 gitignore
。
在本地项目的目录下右键打开Git Bash.
为本地目录初始化一个Git仓库.
1 | $ git init -b main |
将文件添加到你新建的Git仓库中。即在commit之前先暂存 (stage)。
1 | $ git add . |
将暂存在本地仓库中的文件Commit出去。
1 | $ git commit -m "First commit" |
在GitHub仓库的Quick Setup页面复制远程仓库的URL。

回到命令行,将将要push到的远程仓库的URL告诉本地仓库。
1 | $ git remote add origin <REMOTE_URL> |
将本地仓库push到Github侧的远程仓库。
1 | $ git push origin main |
几个文件夹都被顺利commit了。 但是其中的Client文件夹出现了白色的小箭头并且没有办法从github侧直接访问。

(不过用Go to file还是可以access到的:

下载以后发现Client文件夹为空。
原因是该本地文件夹是一个嵌套Git仓库 (nested Git
repository)(详见)。
解决方法是删掉Client里面的.git文件夹,然后执行以下命令重新commit就好了
(以Demo1为例):
1 | $ git rm -r --cached <FILE_NAME> |
1 | $ git add <FILE_NAME> |
可以看到Client侧可以正常访问了。

技术面试的重点。几种常见的数据结构包括:
“C++的==基础知识==,如面向对象的特性、构造函数、析构函数、动态绑定等,能够反映出应聘者是否善于==把握问题本质==,有没有==耐心深入一个问题==。另外还有常用的==设计模式、UML图==等,这些都能体现应聘者是否有==软件工程方面的经验==。” ——王海波(Autodesk,软件工程师)
“对基础知识的考查我特别重视C++中对==内存的使用管理==。我觉得内存管理是C++程序员特别要注意的,因为内存的使用和管理会影响程序的效率和稳定性。” ——蓝诚(Autodesk,软件工程师)
“基础知识反映了一个人的基本能力和基础素质,是以后工作中最核心的能力要求。我一般考查:(1)==数据结构和算法==;(2)==编程能力==;(3)部分==数学知识==,如概率;(4)==问题的分析和推理==能力。” ——张晓禹(百度,技术经理)
“我比较重视四块基础知识:(1)==编程基本功==(特别喜欢字符串处理这一类的问题);(2)==并发控制==;(3)==算法、复杂度==;(4)==语言的基本概念==。” ——张珺(百度,高级软件工程师)
“我会考查编程基础、计算机系统基础知识、算法以及设计能力。这些是一个软件工程师的最基本的东西,这些方面表现出色的人,我们一般认为是有发展潜力的。” ——韩伟东(盛大,高级研究员)
“(1)==对OS的理解程度==。这些知识对于工作中常遇到的==内存管理、文件操作、程序性能、多线程、程序安全==等有重要帮助。对于OS理解比较深入的人对于偏底层的工作上手一般比较快。(2)对于一门==编程语言的掌握程度==。一个热爱编程的人应该会对某种语言有比较深入的了解。通常这样的人对于新的编程语言上手也比较快,而且理解比较深入。(3)常用的==算法和数据结构==。不了解这些的程序员基本只能写写‘Hello World’。” ——陈黎明(微软,SDE II)